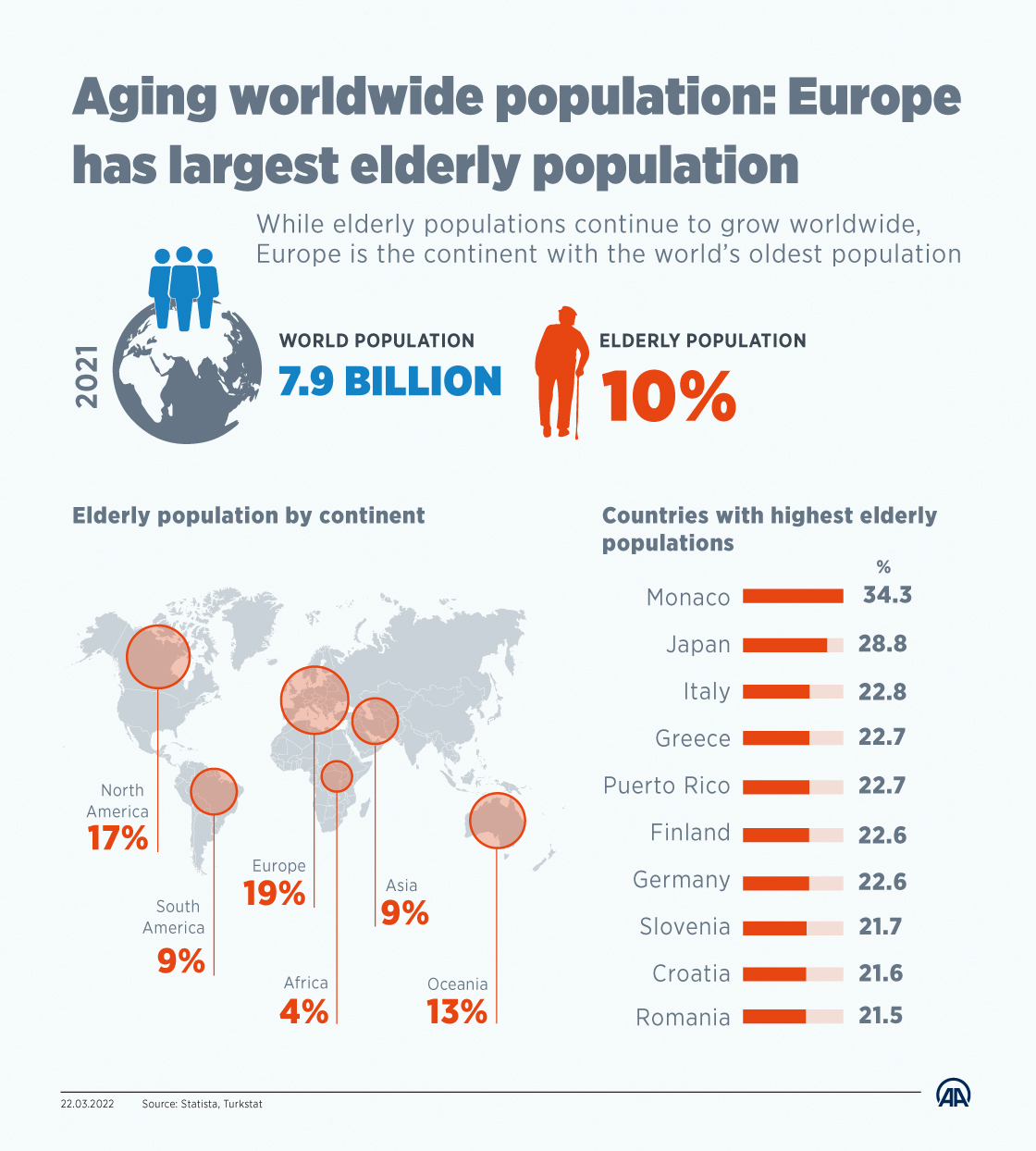
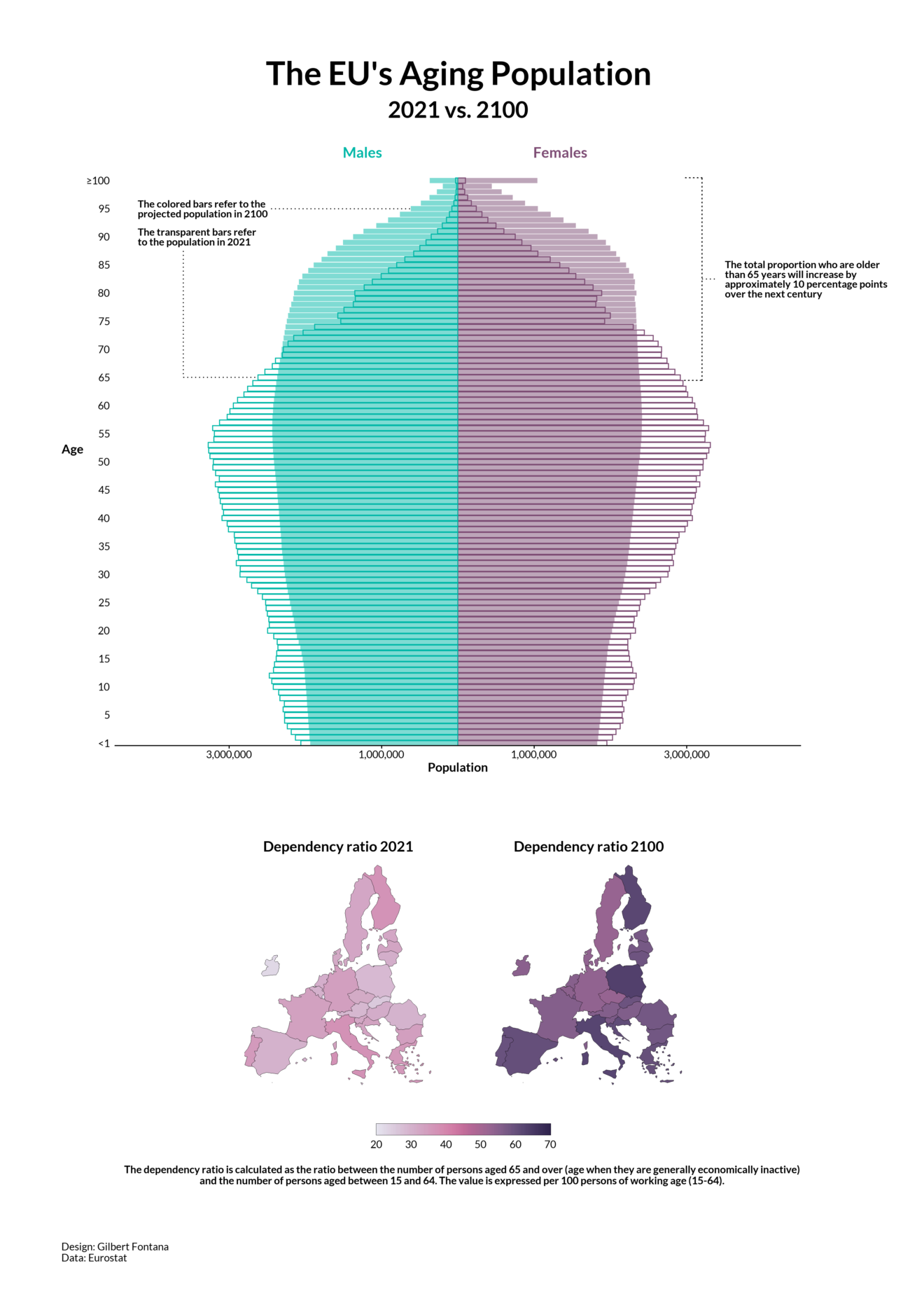
The makeup of a country's people is a big deal, and right now, the changing age of Russia's population is a topic many folks are talking about. This isn't just about numbers on a chart; it's about how daily life works, how a country grows, and what tomorrow might bring. Understanding this shift helps us see a clearer picture of Russia's path ahead, and that, you know, is pretty important.
For a long time, Russia has seen its population figures change quite a bit. There are fewer births and more older people living longer, so the balance is shifting. This trend creates new questions and challenges for communities and for the country's plans. It really does make you think about what kind of world we are building.
This situation isn't unique to Russia, but its scale and specific reasons make it worth a closer look. We'll explore what's happening, why it matters, and what steps might be taken. It's a complex picture, certainly, but one that affects everyone living there, and arguably, the wider world too.
Table of Contents
- The Current Picture of Russia's Population
- Why This Matters So Much
- Looking Ahead: What Can Be Done?
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Current Picture of Russia's Population
When we talk about Russia's aging population, we are really talking about a significant change in how many young people there are compared to older folks. This shift is quite noticeable, and it shapes many aspects of society. It's a bit like a big ship slowly changing course, so the effects take time to fully appear.
The number of people in Russia has seen some ups and downs over the years. Right now, the trend points towards a population that is getting older on average. This means fewer young people entering the workforce and more people needing support in their later years. It’s a pretty big deal, really.
Birth Rates and Death Rates
One main reason for this aging trend is that fewer babies are being born. The birth rate has been on a decline for a while now, and that's a key part of the story. Families, you know, are choosing to have fewer children for various reasons, and this choice has long-term effects on the overall population numbers.
At the same time, people are living longer. Better healthcare and living conditions mean that folks are reaching older ages, which is a good thing in many ways. However, when you combine fewer births with more people living longer, you get a population that is, quite simply, getting older. It's a rather clear pattern, honestly.
This combination creates a demographic squeeze. There are fewer young people to replace the older generations. This imbalance puts pressure on things like pensions and social care systems. It's a situation that requires careful thought and planning, you know, for the years to come.
The reasons for lower birth rates are complex. They can include economic worries, changes in family values, and women having more educational and career opportunities. These are not simple things to change, as a matter of fact. Each factor plays a part in how many children families decide to welcome into the world.
And while people living longer is a positive sign of societal progress, it does mean that the proportion of older citizens grows. This means that, in a way, society needs to adjust its support systems. It's a natural progression, but one that needs a good bit of attention.
Migration Patterns
Migration also plays a role in Russia's population story. People moving into and out of the country can either help or hurt the overall numbers. For instance, if many young people leave, it can make the aging trend even stronger. That's just how it works, apparently.
Historically, Russia has seen various waves of migration. Sometimes people come in from neighboring countries, and sometimes people leave for other parts of the world. These movements can affect the age structure of the population, too it's almost like a constant ebb and flow.
The movement of people can bring new workers and families, which can help to balance out an aging population. However, if the net flow is outward, or if those coming in are also older, then the challenge remains. It's a dynamic factor, and one that is quite important to track.
For example, attracting skilled workers or younger families from other places could help to refresh the population's age profile. But this relies on many things, like economic opportunities and how welcoming a country is. It's not a simple fix, you know, but it is a part of the overall picture.
So, the mix of birth rates, death rates, and how people move around the globe all contribute to the current state of Russia's aging population. It's a multi-layered issue, and understanding each part helps us see the bigger picture. This understanding is, arguably, the first step towards finding solutions.
Why This Matters So Much
An aging population isn't just a statistical curiosity; it has real, tangible effects on a country. These effects can touch almost every part of life, from how much money people earn to how social services are provided. It's a shift that, basically, reshapes society.
The implications are wide-ranging. They affect the economy, social support systems, and even a nation's standing in the world. This is why so many people are talking about it. It really is a topic with a lot of weight, you know.
Economic Challenges
When a population ages, there are fewer working-age people to support a growing number of retirees. This creates a strain on the economy. Fewer workers mean less production and potentially slower economic growth. It's a pretty straightforward cause and effect, in a way.
Think about pensions, for example. If there are fewer people paying into the system and more people drawing from it, the system faces pressure. This can lead to lower pension payments or a need for the government to step in with more funds. It's a very real concern for many older citizens, naturally.
Also, an older workforce might mean less innovation and slower adoption of new technologies. Younger workers often bring fresh ideas and different skills. So, a shrinking pool of young talent can affect a country's competitiveness on the world stage. That's something to consider, certainly.
Healthcare costs also tend to go up with an aging population. Older people generally need more medical care, which puts more demand on hospitals and clinics. This means more money needs to be spent on healthcare, which can strain public budgets. It's a significant financial burden, honestly.
So, the economic challenges are quite clear. Fewer workers, more retirees, and higher healthcare costs all add up to a tough situation for a country's finances. It's a problem that, you know, needs careful handling to avoid bigger issues down the road.
Social Strain
Beyond money, an aging population can also put a strain on social structures. Families might find themselves caring for more elderly relatives, which can be a heavy burden. This often means less time for other things, like raising children or working. It's a shift in family dynamics, definitely.
Communities might also see changes. There might be fewer young families, which can lead to schools closing or a decline in services aimed at children. This can change the whole feel of a neighborhood. It's a bit sad, really, to see communities shrink in that way.
The balance of generations also shifts. There might be fewer young people to volunteer, or to take on certain jobs that require physical effort. This can affect everything from local sports teams to community clean-up efforts. It’s a subtle but important change, as a matter of fact.
Social support systems, like care homes and home care services, face increased demand. Ensuring enough trained staff and suitable facilities becomes a major task. This means that, in some respects, society needs to rethink how it supports its older members, and that takes a lot of effort.
Overall, the social strain is about how people interact, how families function, and how communities thrive. An aging population changes these things in profound ways. It's a challenge that requires a lot of empathy and collective effort, you know, to get right.
Geopolitical Ripples
An aging population can also have effects on a country's standing in the world. Fewer young people might mean a smaller pool for the military, for instance. This can affect a nation's defense capabilities and its ability to project influence. It's a rather serious consideration, certainly.
A country facing internal demographic challenges might also become less focused on external matters. Its leaders might need to spend more time and resources dealing with domestic issues like pensions and healthcare. This can shift priorities, you know, on the global stage.
Economic weakness caused by an aging population can also reduce a country's overall strength. If the economy isn't growing as fast, there's less money for things like research, development, or international aid. This can affect a nation's global standing, pretty much.
Furthermore, an aging society might become more risk-averse. Older populations sometimes prefer stability over bold new ventures. This could affect foreign policy decisions and international relationships. It's a subtle but important factor, arguably, in how a country behaves globally.
So, the geopolitical ripples are about a nation's strength, its influence, and its role in the world. An aging population can change all these things. It's a complex set of connections, and one that many leaders are, quite frankly, thinking about.
Looking Ahead: What Can Be Done?
Facing an aging population is a big task, but countries can take steps to manage the effects. There are different ways to approach this, and many ideas are being discussed. It's about finding smart ways to adapt and plan for tomorrow. This involves, you know, a good bit of foresight.
No single solution will fix everything, but a mix of policies and societal changes can make a difference. It's about building a future where everyone, young and old, can thrive. This requires a lot of collaboration, basically, across different parts of society.
Government Efforts and Policies
Governments often try to encourage higher birth rates. This can involve offering financial help to families, like child benefits or payments for new babies. They might also make childcare more affordable and accessible. These measures are designed to make it easier for people to have children, you know, if they want to.
Some governments also focus on improving healthcare to help people live longer, healthier lives. This includes preventing illnesses and providing good care for older people. A healthy older population can remain active and contribute more to society. This is, in fact, a very important goal.
Another approach is to make it easier for older people to stay in the workforce longer if they choose. This could mean flexible working hours, retraining programs, or removing age-based discrimination. Keeping experienced workers active can help with labor shortages. It's a practical step, certainly.
Governments might also look at immigration policies. Attracting skilled workers or families from other countries can help to boost the working-age population. However, this needs to be managed carefully to ensure smooth integration into society. It's a delicate balance, obviously.
For instance, policies that support young families, like extended parental leave or affordable housing, can make a real difference. These are steps that, you know, aim to create a more supportive environment for raising children. You can learn more about demographic shifts on our site, which can offer more insights.
These government efforts are about creating conditions that help to balance the population's age structure. They are long-term projects, often requiring sustained commitment. It's a continuous process, really, of adjusting and adapting.
Potential Paths for the Future
Beyond government policies, society itself can adapt. For example, communities can create more age-friendly environments, with accessible public transport and social activities for all ages. This helps older people stay connected and active. It's a way to foster stronger communities, you know.
Businesses also have a role to play. They can adapt their products and services to cater to an older population, creating new markets and job opportunities. This might mean different types of housing, healthcare services, or leisure activities. It's about seeing the opportunities, not just the challenges, pretty much.
Technological advancements can also offer solutions. Automation and artificial intelligence might help to offset labor shortages in some sectors. This means that, in a way, technology can help to bridge some of the gaps created by fewer workers. It's an interesting possibility, honestly.
Encouraging lifelong learning and skill development is another path. This helps people of all ages remain adaptable and productive. It means that, you know, people can keep contributing to the economy and society for longer periods. This is beneficial for everyone involved.
The future of Russia's population will depend on how these various efforts come together. It's a challenge that requires creativity, flexibility, and a willingness to change. The aim is to build a resilient society that can thrive, regardless of its age structure. You can also explore global population trends to see how Russia compares to other nations facing similar issues.
As populations shift, countries like Russia face significant decisions. The choices made today will shape the lives of future generations. It's a topic that demands our attention, and one that will continue to evolve. For more detailed information, you might look at reports from organizations like the World Bank, which track global demographic data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of Russia's aging population?
The primary causes are a low birth rate, meaning fewer babies are being born each year, and an increasing life expectancy. This combination leads to a higher proportion of older people compared to younger ones. It's a pretty clear demographic trend, so.
How does an aging population affect Russia's economy?
An aging population can slow economic growth because there are fewer working-age people to contribute to the workforce. This also puts pressure on pension systems and increases healthcare costs. It's a significant financial challenge, you know, for the country's budget.
What steps is Russia taking to address its demographic challenges?
Russia is implementing various policies to encourage higher birth rates, such as offering financial support to families and improving childcare options. They are also looking at ways to extend working lives and manage migration. These are efforts to balance the age structure, apparently.